
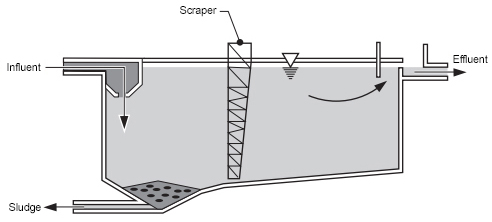
Large weir overflow rates result in excessive velocities at the outlet. However, peripheral weirs are not acceptable as they tend to cause excessive short-circuiting. Weirs shall be adjustable, and at least equivalent in length to the perimeter of the tank. Outlet Devices: Outlet weirs or submerged orifices shall be designed to maintain velocities suitable for settling in the basin and to minimize short-circuiting. A baffle should be constructed across the basin close to the inlet and should project several feet below the water surface to dissipate inlet velocities and provide uniform flow Inlet devices: Inlets shall be designed to distribute the water equally and at uniform velocities. Sludge zone: For collection of sludge below settling zone. Outlet zone: Clarified effluent is collected and discharge through outlet weir. Settling zone: Settling occurs under quiescent conditions. Inlet zone: Region in which the flow is uniformly distributed over the cross section such that the flow through settling zone follows horizontal path. A slow moving mechanical sludge scraper continuously pulls the settled material into a sludge hopper from where it is pumped out periodically.Ī long rectangular settling tank can be divided into four different functional zones: The bottom is slightly sloped to facilitate sludge scraping. A typical long rectangular tank have length ranging from 2 to 4 times their width.

Long rectangular basins are hydraulically more stable, and flow control for large volumes is easier with this configuration.For laminar, transition, and turbulent flow, the values of C D are: This force, called the drag force, is quantified by:īecause the drag force acts in the opposite direction to the driving force and increases as the square of the velocity, accelaration occurs at a decreasing rate until a steady velocity is reached at a point where the drag force equals the driving force:Įxpressions for C D change with characteristics of different flow regimes. Once the motion has been initiated, a third force is created due to viscous friction. This net force becomes the driving force. If the density of the particle differs from that of the water, a net force is exerted and the particle is accelaratd in the direction of the force: (2) the buoyant force quantified by Archimedes as: F b= rgV p If a particle is suspended in water, it initially has two forces acting upon it:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
